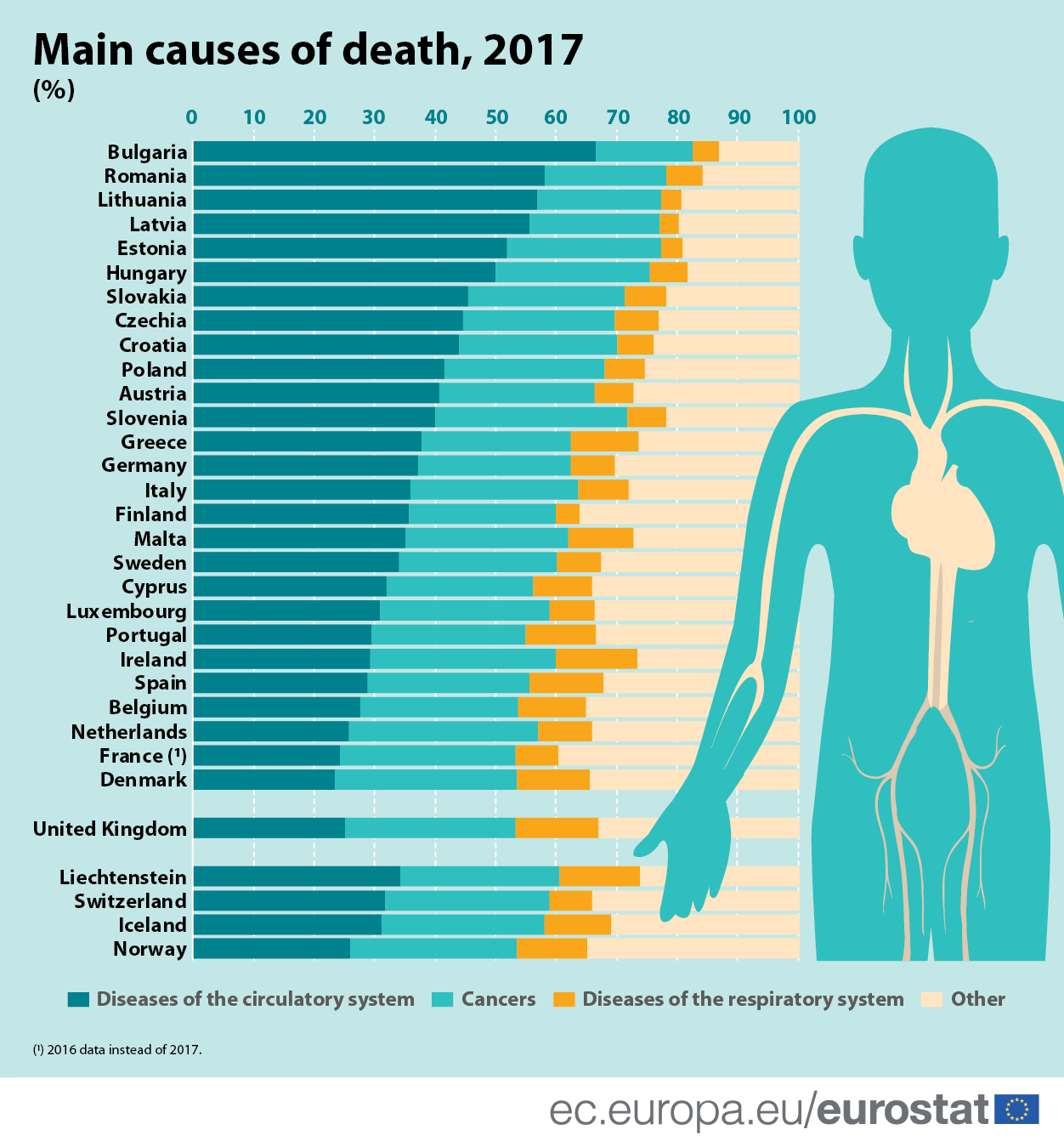
Understanding the causes of death is crucial for advancing public health initiatives, guiding medical research, and fostering informed decision-making among individuals and families. The causes of death can vary significantly based on a multitude of factors including geographical location, socioeconomic status, lifestyle choices, and medical advancements. In this article, we will delve into various aspects of causes of death, ranging from common diseases to external factors like accidents and violence.
We will explore statistical data, provide insights into different demographics, and examine the impact of lifestyle choices on mortality rates. Our goal is to provide readers with a thorough understanding of how and why people die, which is essential for both personal awareness and broader societal implications.
This article will also highlight key statistics and research findings, offering a well-rounded perspective on causes of death globally. By the end of this exploration, readers will not only be informed about the leading causes of mortality but also equipped with knowledge that can influence their health decisions and advocacy efforts.
- Is Andrea Bocelli Ill Understanding His Health Journey
- Understanding Pet Food A Comprehensive Guide For Pet Owners
Table of Contents
- 1. Overview of Causes of Death
- 2. Leading Causes of Death Worldwide
- 3. Causes of Death by Age Group
- 4. Impact of Lifestyle Choices
- 5. The Role of Healthcare Access
- 6. External Causes of Death
- 7. Emerging Trends in Mortality
- 8. Conclusion and Call to Action
1. Overview of Causes of Death
The causes of death can be broadly categorized into two groups: natural causes and external causes. Natural causes include diseases and medical conditions, while external causes involve injuries, accidents, and violence. Understanding these categories is essential for public health professionals and policymakers as they develop strategies to reduce mortality.
Natural Causes of Death
Natural causes of death typically arise from diseases and health conditions, such as:
- Heart disease
- Cancer
- Chronic respiratory diseases
- Stroke
- Alzheimer's disease
External Causes of Death
External causes encompass a range of factors that lead to premature death, including:
- Selena Gomez Show A Deep Dive Into Her Impact On Entertainment
- Bob Saget Movies And Tv Shows A Comprehensive Guide To His Career
- Accidents (e.g., car crashes, falls)
- Suicides
- Homicides
- Drug overdoses
2. Leading Causes of Death Worldwide
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the leading causes of death vary between regions but certain diseases consistently rank high globally. In 2021, the following were identified as the top causes of death:
- Ischemic heart disease
- Stroke
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Lower respiratory infections
- Neonatal conditions
This data highlights the importance of focusing on cardiovascular health and respiratory diseases in public health initiatives.
3. Causes of Death by Age Group
The causes of death can vary significantly based on age demographics. Understanding these differences is vital for targeting health interventions effectively.
Infants and Children
In infants and young children, the leading causes of death often include:
- Neonatal conditions
- Diarrheal diseases
- Pneumonia
Adults
For adults, particularly those aged 30-60, the primary causes of death typically include:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Cancers
- Diabetes
Older Adults
Among older adults, the leading causes of death shift towards:
- Alzheimer's disease
- Heart disease
- Cancer
4. Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in determining health outcomes and mortality rates. Factors such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption can significantly influence the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Diet and Nutrition
A poor diet, high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, is linked to several health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Conversely, a balanced diet can reduce the risk of these conditions.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is associated with a lower risk of mortality. The WHO recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week to maintain health.
5. The Role of Healthcare Access
Access to healthcare services is a critical factor in determining health outcomes. Populations with limited access to healthcare are more likely to experience higher rates of mortality from preventable diseases.
Preventive Care
Preventive care, including vaccinations and regular health screenings, plays a significant role in reducing deaths from common diseases. Public health initiatives aimed at increasing access to preventive services are essential.
Health Insurance
Having health insurance can greatly improve an individual's ability to seek timely medical care, which is vital for early detection and treatment of health issues.
6. External Causes of Death
External causes of death, such as accidents and violence, are significant contributors to mortality rates, especially among younger populations.
Accidents
Accidental deaths, including those from vehicle crashes and falls, account for a substantial percentage of fatalities, particularly in younger age groups.
Violence and Suicide
Violence, including homicide and suicide, poses a significant public health challenge. Mental health initiatives and community programs are crucial for addressing these issues.
7. Emerging Trends in Mortality
Recent years have seen emerging trends in causes of death, influenced by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and rising substance abuse rates. It is essential to stay informed about these trends for effective public health planning.
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped mortality statistics globally, highlighting the importance of infectious disease preparedness and response.
Substance Abuse
Increased rates of drug overdoses have become a significant concern, particularly with the rise of synthetic opioids. Addressing this crisis requires comprehensive public health strategies.
8. Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the causes of death is vital for improving public health outcomes and guiding policy decisions. By being aware of the leading causes of death and the factors that contribute to them, individuals can make informed choices that promote better health.
We encourage readers to take action by prioritizing their health, advocating for accessible healthcare, and supporting public health initiatives aimed at reducing mortality rates.
For further information, feel free to leave a comment, share this article, or explore additional resources on our site. Together, we can work towards a healthier future.
- Exploring The Life And Legacy Of Earvin Johnson A Basketball Icon
- Chickfila Breakfast A Complete Guide To The Morning Menu